Last update:
Laboratory medicine news
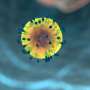
Dynamic gel helps scientists grow organs more reliably in the lab
Miniature organs grown in the lab can organize themselves into complex shapes. But they never do it the same way twice, which makes it hard to use these so-called "organoids" to study disease. Now, scientists at UC San Francisco ...
Mar 11, 2026
0
0
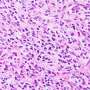
Optical genome mapping detects additional genetic variants in nearly 20% of individuals with acute leukemia
New research assessing the efficacy of optical genome mapping (OGM) in a group of patients with acute leukemia has demonstrated that OGM provided reliable and robust analytical performance with high sensitivity and specificity ...
Mar 11, 2026
0
0
Real-time metabolic monitoring on a chip: What happens inside a cell can be measured instantly
In a significant advancement for lab-on-chip technology, IBEC researchers in the frame of the European project BLOC, have demonstrated the first integration of a benchtop nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer with ...
Mar 10, 2026
0
0

Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
With aging populations on the rise, the need for better tools to diagnose and monitor Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common cause of dementia, has never been more urgent. This disease is characterized by the gradual loss ...
Mar 10, 2026
0
0

Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
An antibody test for the infectious disease mpox was successfully developed during the new clade 1b outbreak in Rwanda, the first time that an assay of its kind has been validated within this setting. The test, an IgG ELISA ...
Mar 9, 2026
0
0

HIV-seq tool finds active reservoir cells during therapy
For people living with human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), life-saving antiretroviral therapy keeps their HIV-infected immune cells from making new copies of the virus, preventing illness and transmission. Historically, these ...
Mar 7, 2026
0
0

Cheek cells may provide clues to schizophrenia risk
A simple cheek swab could one day provide a quick and noninvasive diagnostic test for schizophrenia. A new study published in Science Advances has identified higher levels of two biological markers in the cheek swabs of patients ...

Blood-based marker opens up perspectives for cancer diagnostics
Metastatic prostate cancer is currently associated with high morbidity and mortality rates. In addition, patients respond very differently to standard treatments such as hormone therapy or radiation therapy. Reliable markers ...
Mar 6, 2026
0
0

AI blood test detects early pancreatic cancer with up to 94% accuracy
A team of researchers from Taiwan has developed PanMETAI, an AI-powered platform that analyzes metabolic fingerprints in a simple blood sample to detect pancreatic cancer at its earliest stages—when treatment is most effective—achieving ...
Mar 5, 2026
0
4

Early detection of brain disorders with a single drop of saliva
A team of Korean researchers has, for the first time, developed a technology capable of enabling early diagnosis of major neurological disorders including epilepsy, Parkinson's disease, and schizophrenia using only a small ...
Mar 5, 2026
0
1

Portable CRISPR-based test detects four STIs, including syphilis, in under an hour
Researchers at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute) have developed a world-first portable point-of-care test that detects four common sexually transmitted infections at once, in under ...
Mar 4, 2026
0
0

AI-based liquid biopsy may detect liver fibrosis, cirrhosis and chronic disease signals
Researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center report that an artificial intelligence (AI)-based liquid biopsy test using genome-wide cell-free DNA (cfDNA) fragmentation patterns and repeat landscapes can detect early ...
Mar 4, 2026
0
0

One-hour saliva test spots biomarker linked to several cancers
QUT researchers have developed a simple one-hour saliva test for a protein biomarker that has been linked with oral, colon and pancreatic cancers. The findings are published in the journal Talanta.
Mar 4, 2026
0
0

From dementia to diabetes: New tool tracks disordered proteins in solution
A DGIST research team led by Prof. Yoo Wookyung (Department of Brain Sciences) and Prof. Kim Jin Hae (Department of New Biology) developed an innovative analytical technology in collaboration with a research team led by Dr. ...
Mar 4, 2026
0
0

Pathogen-agnostic testing reveals hidden respiratory threats in negative samples
The COVID-19 pandemic brought the term "Polymerase Chain Reaction testing" into the mainstream. The PCR method is a type of nucleic acid amplification test (NAAT) that detects a pathogen by finding and amplifying components ...
Mar 3, 2026
0
0

Tiled amplicon sequencing could transform tuberculosis care
When the COVID-19 pandemic was at its peak, and multiple variants were threatening lives around the world, scientists relied on a process called "tiled amplicon sequencing" to track the virus's spread. Now, an international ...
Mar 3, 2026
0
0

Specific protein and sugar molecules affected by aging and disease identified
Neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease (AD) are typically diagnosed after irreversible pathology has developed. Aging, the strongest risk factor, drives molecular changes that predispose the brain to synaptic ...
Mar 3, 2026
0
0

AI cancer tools may rely on 'shortcut learning' rather than genuine biological signals
Artificial intelligence tools are increasingly being developed to predict cancer biology directly from microscope images, promising faster diagnoses and cheaper testing. But new research from the University of Warwick, published ...
Mar 2, 2026
0
0

New diagnostic markers for multiple sclerosis discovered in cerebrospinal fluid
Researchers from the MPI of Biochemistry and the Technical University of Munich have discovered new diagnostic markers for multiple sclerosis (MS), a disease that affects 3 million people worldwide. Using mass spectrometry, ...
Mar 2, 2026
0
0

A new class of Alzheimer's biomarkers: Why protein shape may beat protein levels
Researchers have identified a new type of blood-based biomarker test for Alzheimer's disease that measures structural changes in proteins, providing more information on the underlying biology of the disease than standard ...
Mar 2, 2026
0
0

Cell-free DNA offers early warning for bloodstream infections in kids with leukemia
Researchers have identified a promising way to predict bloodstream infections in children with high-risk leukemia days before the infection would be diagnosed using current standards of care. The test, named plasma microbial ...
Mar 2, 2026
0
0

Multidisciplinary study uses blood samples to identify diseases years before they start
What if doctors could tell you a disease was coming years before you felt a single symptom—and stop it in its tracks? That is the goal of a sweeping new research initiative launched by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount ...
Mar 2, 2026
0
0

Houston, we have a problem: Study points to clotting glitch in space
A cut presumably draws blood anywhere in the universe, whether in an Earthly suburb or on some future interstellar voyage yet undreamed outside science fiction. In space, however, clotting's the challenge. A recent study ...
Feb 26, 2026
0
0

Gallbladder cancer could soon be detected in blood
Researchers at Tezpur University in Assam, India, working with scientists at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign, have identified distinct chemical signatures in blood that could help detect gallbladder cancer earlier. ...
Feb 25, 2026
0
0

New 'liver-on-a-chip' device could make drug safety testing more reliable
Creating a drug that might help treat or cure a health condition in humans is a long, complex process. After developing a candidate drug that shows potential—a process that, in and of itself, can take decades—scientists ...
Feb 23, 2026
0
14